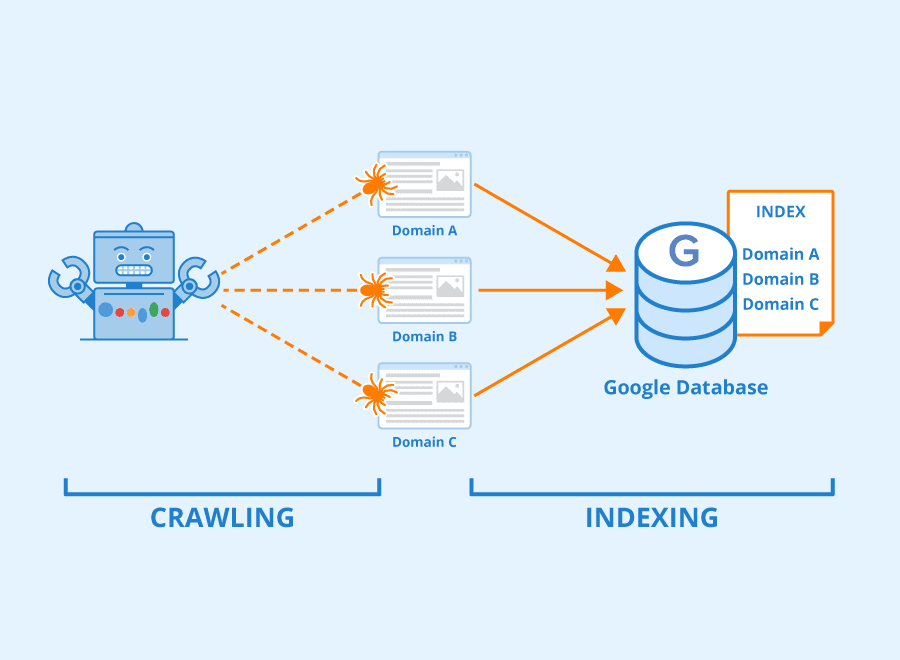
In the intricate world of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), two fundamental processes—crawling and indexing—lay the foundation for a website’s visibility in search results.
Understanding how search engines crawl and index web pages is crucial for optimizing your online presence.
In this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the intricacies of crawling and indexing, exploring their significance and providing insights into how you can leverage these processes to enhance your SEO strategy.
Crawling: The Exploration Phase
1. Defining Crawling:
- Crawling is the process by which search engines systematically browse the web to discover and gather information about web pages. Search engine bots, commonly known as spiders or crawlers, visit websites, follow links, and collect data on the content and structure of each page.
2. How Crawlers Work:
- Crawlers start with a list of known web pages and use links to navigate from one page to another. They analyze the content, follow hyperlinks, and index information about each page they encounter. The frequency of crawling varies, with more popular and frequently updated pages being crawled more often.
3. Optimizing for Crawlers:
- Ensure that all pages you want search engines to index are accessible to crawlers. Use a sitemap to provide a structured overview of your website’s content and consider the use of a robots.txt file to guide crawlers on which pages to crawl or avoid.
Indexing: Organizing the Web
1. Defining Indexing:
- Indexing is the process of storing and organizing the information gathered during crawling. The search engine creates an index, a massive database containing data about the content and relevance of each web page. This index serves as the foundation for delivering search results.
2. How Indexing Works:
- Once a search engine crawler has collected data from web pages, it organizes and stores this information in its index. The index is a structured database that allows the search engine to quickly retrieve relevant information in response to user queries.
3. Optimizing for Indexing:
- Create high-quality, relevant content that aligns with user intent. Ensure proper use of keywords, meta tags, and structured data to provide search engines with clear signals about the content of your pages.
The Symbiotic Relationship:
- Crawling and Indexing Dynamics:
- Crawling and indexing work hand in hand. Crawlers discover and collect information during the crawling phase, and the indexed data serves as the basis for delivering search results. Regular crawling ensures that the index is updated with the latest information.
- Fresh Content and Recrawling:
- Search engines prioritize frequently updated and fresh content. Regularly adding new content and updating existing pages signals to crawlers that recrawling is necessary, ensuring that your website’s information remains current in the index.
Common Issues and Solutions:
- Crawl Errors:
- Monitor crawl errors using tools like Google Search Console to identify issues that may hinder crawling, such as broken links or inaccessible pages. Addressing these issues ensures a smooth crawling process.
- Indexation Issues:
- If certain pages are not appearing in search results, investigate potential indexation issues. Check the robots.txt file and meta robots tags to ensure that pages are not unintentionally excluded from indexing.
Conclusion
Crawling and indexing form the backbone of search engine success. By understanding these processes and optimizing your website to facilitate efficient crawling and indexing, you pave the way for enhanced visibility in search results.
Stay attuned to industry best practices, regularly monitor your website’s performance, and leverage these fundamental processes to propel your online presence to new heights in the competitive digital landscape.